Business Management IA: Real Company Analysis Strategies
Struggling to choose a company or figure out how to analyze it for your IB Business Management Internal Assessment (IA)? You're not alone! The IA is a significant component of your final IB grade, and a well-executed real company analysis is crucial for success. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of strategies you can use to effectively analyze a real company for your IB Business Management IA. We'll cover everything from selecting the right company to conducting in-depth financial analysis and crafting a compelling report. By the end of this guide, you'll have the tools and knowledge you need to confidently tackle your IA and achieve a top score.
Choosing the Right Company: Setting the Stage for Success
Selecting the right company is the first, and arguably most important, step in your IB Business Management IA journey. The company you choose should be relevant to your chosen topic, accessible in terms of data, and offer sufficient complexity for in-depth analysis.
Relevance to Your Research Question
Your chosen company must be relevant to the research question you're investigating. For example, if your research question focuses on the impact of globalization on a specific industry, you'll need to select a company that operates internationally and has been affected by globalization trends. A local, small business might not provide enough scope for a meaningful analysis.
- Example: If your research question is "To what extent has the implementation of lean production impacted the operational efficiency of Toyota?", Toyota would be an obvious and relevant choice.
Data Accessibility: Avoiding Dead Ends
Ensure that sufficient data is publicly available about the company. This includes financial statements (balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements), annual reports, news articles, and industry reports. Without access to reliable data, your analysis will be severely limited.
- Tip: Check the company's investor relations website for financial information. Also, explore databases like Bloomberg, Reuters, or even Google Finance for publicly available data.
Complexity: Striking the Right Balance
The company should be complex enough to allow for in-depth analysis but not so complex that it becomes overwhelming. A multinational corporation with diverse operations and a long history will likely offer more opportunities for analysis than a small, newly established business.
- Example: Analyzing Apple's supply chain or marketing strategies would provide ample material for a strong IA, given its global reach and innovative practices.
Ethical Considerations
Always consider the ethical implications of your chosen company and research question. Avoid companies with a history of unethical practices or controversial business dealings, as this could raise concerns about bias and objectivity in your analysis.
Struggling with IB Assessments?
Get instant, detailed feedback on your work with AI that understands IB criteria.
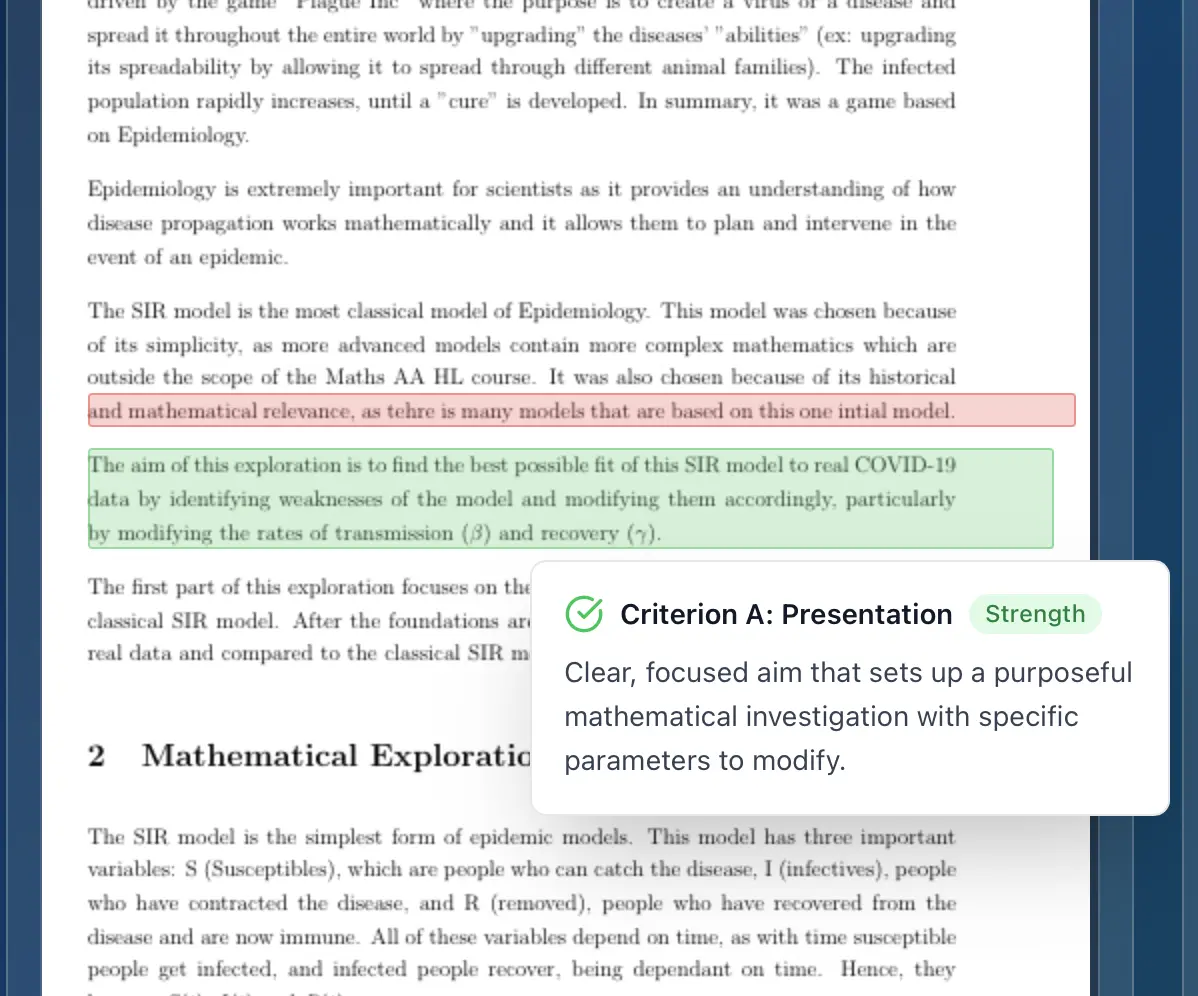
Core Analysis Strategies: Diving Deep into the Data
Once you've selected your company, it's time to start analyzing its performance and strategies. Here are some core analysis strategies you can use in your IB Business Management IA:
Financial Ratio Analysis: Unveiling the Numbers
Financial ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting various financial ratios to assess a company's profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. This is a fundamental aspect of business analysis.
-
Profitability Ratios:
- Gross Profit Margin: (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100 - Measures the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold.
- Net Profit Margin: (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100 - Measures the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses.
- Return on Equity (ROE): (Net Profit / Shareholders' Equity) x 100 - Measures the return generated on shareholders' investment.
-
Liquidity Ratios:
- Current Ratio: Current Assets / Current Liabilities - Measures a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations.
- Quick Ratio (Acid Test): (Current Assets - Inventory) / Current Liabilities - A more conservative measure of liquidity, excluding inventory.
-
Solvency Ratios:
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Total Debt / Shareholders' Equity - Measures the proportion of debt financing relative to equity financing.
-
Efficiency Ratios:
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory - Measures how efficiently a company manages its inventory.
- Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: Revenue / Average Accounts Receivable - Measures how efficiently a company collects its receivables.
-
Example: Analyzing the trend in Apple's gross profit margin over the past five years can reveal insights into its pricing power and cost management strategies.
SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the internal strengths and weaknesses of a company, as well as the external opportunities and threats it faces.
-
Strengths: Internal factors that give the company a competitive advantage.
-
Weaknesses: Internal factors that hinder the company's performance.
-
Opportunities: External factors that the company can exploit to its advantage.
-
Threats: External factors that pose a risk to the company's performance.
-
Example: A SWOT analysis of Tesla might identify its strong brand reputation and technological innovation as strengths, its high production costs as a weakness, the growing demand for electric vehicles as an opportunity, and increasing competition from established automakers as a threat.
PESTLE Analysis: Understanding the External Environment
PESTLE analysis is a framework used to analyze the macro-environmental factors that can affect a company's performance.
-
Political: Government policies, regulations, and political stability.
-
Economic: Economic growth, inflation, interest rates, and exchange rates.
-
Social: Cultural trends, demographics, and consumer attitudes.
-
Technological: Technological advancements, innovation, and automation.
-
Legal: Laws and regulations related to business operations.
-
Environmental: Environmental regulations, sustainability concerns, and climate change.
-
Example: A PESTLE analysis of the airline industry might consider the impact of government regulations on air travel, the effects of economic recessions on demand, the influence of social media on brand reputation, the role of technological advancements in aircraft efficiency, the legal implications of air safety regulations, and the environmental concerns related to carbon emissions.
Porter's Five Forces: Analyzing Industry Competitiveness
Porter's Five Forces is a framework used to analyze the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry.
-
Threat of New Entrants: The ease with which new competitors can enter the industry.
-
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: The ability of suppliers to raise prices or reduce the quality of their products.
-
Bargaining Power of Buyers: The ability of buyers to negotiate lower prices or demand better products.
-
Threat of Substitute Products or Services: The availability of alternative products or services that can satisfy the same customer needs.
-
Rivalry Among Existing Competitors: The intensity of competition among existing firms in the industry.
-
Example: Applying Porter's Five Forces to the fast-food industry might reveal that the threat of new entrants is relatively low due to high capital requirements and brand loyalty, the bargaining power of suppliers is moderate, the bargaining power of buyers is high due to the availability of many alternatives, the threat of substitute products is high due to the availability of home-cooked meals and other dining options, and the rivalry among existing competitors is intense due to the large number of players and price competition.
Common Challenges/Mistakes: Avoiding Pitfalls
Many students encounter similar challenges when working on their IB Business Management IA. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Lack of Focus: Choosing a research question that is too broad or vague. Ensure your research question is specific and focused.
- Insufficient Data: Selecting a company with limited publicly available data. Always verify data availability before committing to a company.
- Superficial Analysis: Conducting a shallow analysis that lacks depth and critical thinking. Go beyond simply stating facts and figures; interpret their significance.
- Descriptive vs. Analytical: Focusing on describing what happened rather than analyzing why it happened and its implications.
- Poor Structure and Organization: Presenting your analysis in a disorganized and confusing manner. Use clear headings, subheadings, and transitions to guide the reader.
- Ignoring Ethical Considerations: Failing to address the ethical implications of your chosen company or research question.
- Plagiarism: Presenting someone else's work as your own. Always cite your sources properly.
Pro Tip: Get AI-Powered Grading
Stop second-guessing your grades. Get instant feedback aligned with official IB rubrics.
Advanced Tips/Strategies: Elevating Your Analysis
To take your IB Business Management IA to the next level, consider these advanced tips and strategies:
- Primary Research: Supplement your secondary research with primary research, such as conducting interviews with industry experts or surveying customers.
- Qualitative Data: Incorporate qualitative data, such as case studies, industry reports, and expert opinions, to provide a more nuanced understanding of the company and its environment.
- Critical Evaluation: Critically evaluate the sources you use and consider their biases and limitations.
- Trend Analysis: Analyze trends over time to identify patterns and predict future performance.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare the company's performance to that of its competitors or industry benchmarks.
- Scenario Planning: Develop different scenarios to assess the potential impact of various external factors on the company's performance.
- Recommendations: Provide clear and actionable recommendations based on your analysis.
Technology and Modern Assessment: Leveraging AI for Success
Technology is transforming the way we approach business analysis and assessment. AI-powered tools can help you streamline your research, analyze data more efficiently, and improve the quality of your work.
For example, AI can be used to automate data collection, identify patterns in financial data, and generate insights from large datasets. Furthermore, AI is revolutionizing the way assessments are graded and feedback is provided.
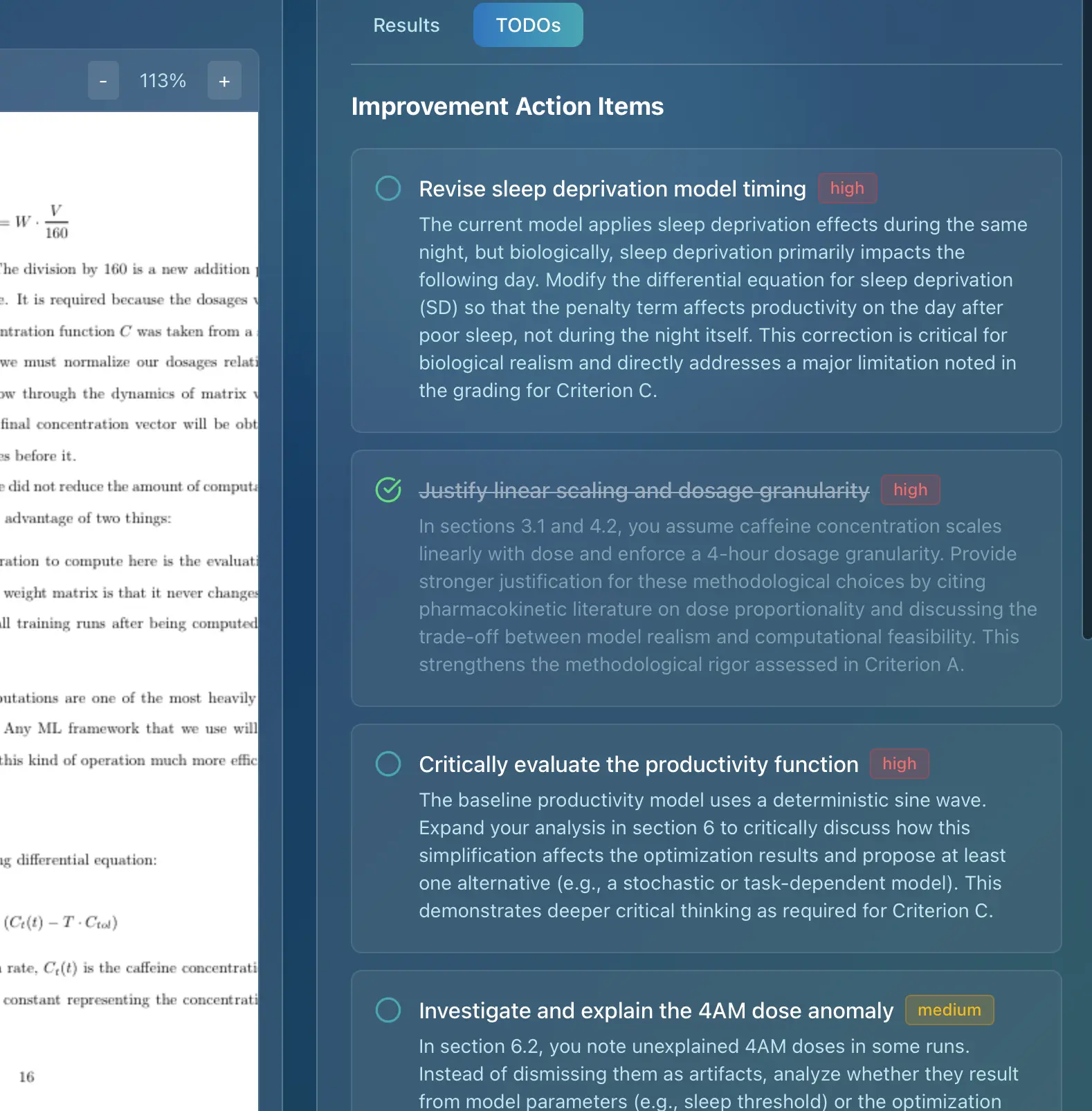
Marksy, as a leading AI grading assistant specifically designed for the International Baccalaureate, helps teachers provide consistent, detailed feedback on IB assessments. Marksy uses official IB rubrics to ensure accuracy and fairness, providing criterion-by-criterion feedback and suggestions for improvement. This not only saves educators valuable time but also helps students understand exactly how to improve their work and achieve higher scores. By leveraging AI, teachers can focus on providing personalized support and guidance to their students, while ensuring that assessments are fair, accurate, and aligned with IB standards.
Conclusion with Clear Next Steps
The IB Business Management IA is a challenging but rewarding task. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can confidently analyze a real company and produce a high-quality report that demonstrates your understanding of business concepts and analytical skills. Remember to choose a relevant company, conduct in-depth analysis, avoid common mistakes, and leverage technology to enhance your work.
Next Steps:
- Choose your company and research question: Start brainstorming potential companies and research questions that align with your interests and the IB Business Management syllabus.
- Gather data: Begin collecting financial statements, annual reports, and other relevant data about your chosen company.
- Conduct your analysis: Apply the analysis strategies discussed in this guide to gain insights into the company's performance and strategies.
- Structure your report: Organize your analysis in a clear and logical manner, using headings, subheadings, and transitions to guide the reader.
- Seek feedback: Ask your teacher or a peer to review your work and provide feedback.
- Try Marksy for free: Sign up for a free trial of Marksy to experience the benefits of AI-powered grading and feedback. See how Marksy can help you improve your IB scores or streamline your grading workflow. [Link to Marksy Free Trial]
Good luck with your IB Business Management IA!