Computer Science IA: Best Programming Languages for IB Students
Choosing the right programming language for your IB Computer Science Internal Assessment (IA) is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your grade. With so many options available, it's essential to select a language that not only aligns with your skills but also allows you to effectively demonstrate your understanding of computer science principles and meet the IB's rigorous assessment criteria. This guide will explore the best programming languages for IB students, providing insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for different IA projects. We'll also offer practical tips and strategies to help you make an informed decision and maximize your IA score.
Introduction: Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
The IB Computer Science IA is your opportunity to showcase your programming skills and problem-solving abilities. Selecting the right programming language is like choosing the right tool for a specific job – it can make the task significantly easier and more efficient. This decision should be based on several factors, including your familiarity with the language, the complexity of your project, and the language's suitability for the chosen application. A well-chosen language can help you achieve a higher score by allowing you to focus on the core computer science concepts and demonstrate your understanding of algorithmic thinking, data structures, and software development principles.
Struggling with IB Assessments?
Get instant, detailed feedback on your work with AI that understands IB criteria.
Core Content Sections
Python: The Versatile Choice
Python is often recommended as an excellent starting point for IB Computer Science students. Its clear syntax and extensive libraries make it a versatile choice for a wide range of projects.
- Strengths:
- Readability: Python's syntax is easy to understand, making your code more maintainable and easier for the examiner to follow.
- Extensive Libraries: Python boasts a vast collection of libraries for various applications, including data science (NumPy, Pandas), web development (Flask, Django), and game development (Pygame).
- Large Community Support: A large and active community provides ample resources, tutorials, and support for Python developers.
- Weaknesses:
- Performance: Python can be slower than compiled languages like Java or C++ for computationally intensive tasks.
- Typing: Python is dynamically typed, which can sometimes lead to runtime errors if not carefully managed.
- Suitable Projects:
- Data analysis and visualization projects
- Web applications
- Simple games
- AI and machine learning projects
Example: A student could use Python with the Flask framework to create a web application that allows users to track their fitness goals.
Java: The Object-Oriented Powerhouse
Java is a robust and widely used language that excels in object-oriented programming. It's a great choice if your project requires complex data structures and algorithms.
- Strengths:
- Object-Oriented: Java's strong support for object-oriented principles allows you to create modular and reusable code.
- Platform Independence: Java's "write once, run anywhere" capability makes it suitable for projects that need to run on different operating systems.
- Large Ecosystem: Java has a mature ecosystem with a wealth of libraries and frameworks.
- Weaknesses:
- Verbosity: Java code can be more verbose than Python, requiring more lines of code to achieve the same functionality.
- Complexity: Java can be more complex to learn than Python, especially for beginners.
- Suitable Projects:
- Desktop applications
- Mobile applications (Android)
- Enterprise applications
- Game development (using libraries like LibGDX)
Example: A student could use Java to develop a desktop application for managing a library's inventory.
C++: The Performance Champion
C++ is a powerful language that offers excellent performance and control over hardware resources. It's a good choice for projects that require high performance or low-level access.
- Strengths:
- Performance: C++ is known for its speed and efficiency, making it suitable for performance-critical applications.
- Low-Level Control: C++ allows you to directly manipulate memory and hardware resources.
- Large Community: C++ has a large and active community, providing ample resources and support.
- Weaknesses:
- Complexity: C++ is a complex language with a steep learning curve.
- Memory Management: C++ requires manual memory management, which can be error-prone.
- Suitable Projects:
- Game development (especially for high-performance games)
- Operating systems
- Embedded systems
- Scientific simulations
Example: A student could use C++ to develop a game engine or a simulation of a physical system.
JavaScript: The Web Frontrunner
JavaScript is the dominant language for front-end web development and is increasingly used for back-end development as well (Node.js).
- Strengths:
- Ubiquity: JavaScript runs in web browsers, making it ideal for creating interactive web applications.
- Frameworks: Numerous JavaScript frameworks (React, Angular, Vue.js) simplify web development.
- Full-Stack Development: With Node.js, you can use JavaScript for both front-end and back-end development.
- Weaknesses:
- Security: JavaScript can be vulnerable to security exploits if not carefully coded.
- Debugging: Debugging JavaScript can be challenging due to its dynamic nature.
- Suitable Projects:
- Interactive websites
- Web applications
- Mobile applications (using frameworks like React Native)
- Games (using libraries like Phaser)
Example: A student could use JavaScript with React to create an interactive website for showcasing their portfolio.
Common Challenges/Mistakes Section
Choosing the wrong language is a common mistake. Students often pick a language they think is impressive, even if they lack proficiency. This leads to poorly implemented projects and lower scores. Here are some other common pitfalls:
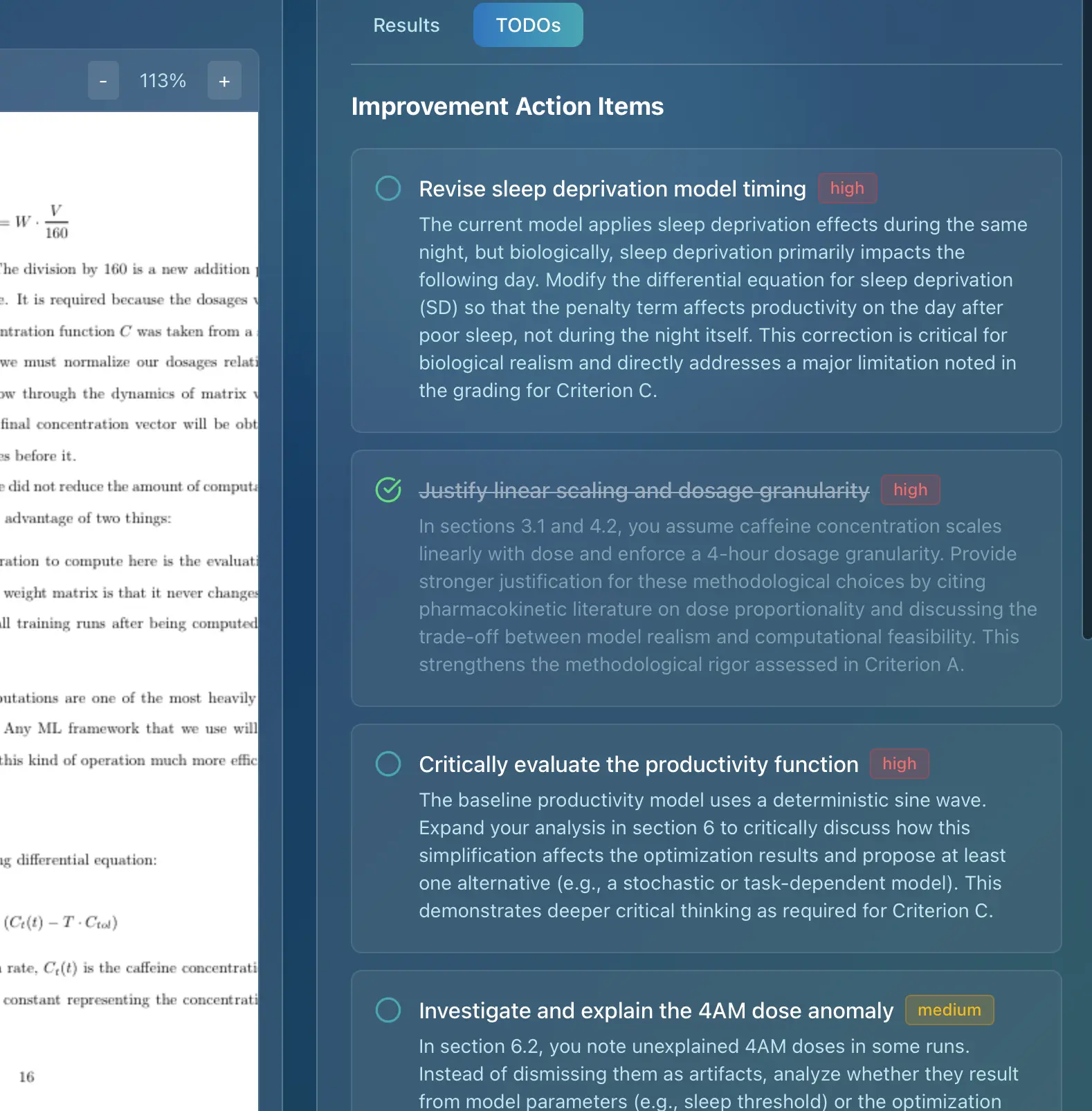
- Overly Ambitious Projects: Don't try to tackle a project that's too complex for your skill level. Focus on a smaller, well-defined project that you can execute effectively. Remember Criterion A: Planning. A well-defined scenario and measurable success criteria are key.
- Poor Planning: Failing to plan your project thoroughly can lead to wasted time and effort. Create a detailed plan outlining your goals, tasks, and timeline. This directly impacts Criterion B: Solution Overview. A detailed record of tasks and design overview is crucial.
- Inadequate Testing: Thoroughly test your code to identify and fix bugs. A comprehensive outline test plan is essential for a good score in Criterion B.
- Lack of Documentation: Document your code clearly and concisely. This will make it easier for the examiner to understand your work and award you marks.
- Ignoring the IB Criteria: Make sure you understand the IB's assessment criteria and tailor your project accordingly. Pay close attention to Criterion C: Development. The use of techniques should demonstrate a high level of complexity and ingenuity.
Solution: Start with a simple prototype to validate your ideas and gradually add complexity as you progress. Regularly seek feedback from your teacher or advisor to ensure you're on the right track.
Pro Tip: Get AI-Powered Grading
Stop second-guessing your grades. Get instant feedback aligned with official IB rubrics.

Advanced Tips/Strategies Section
To excel in your IB Computer Science IA, consider these advanced tips:
- Focus on Algorithmic Thinking: Demonstrate your ability to design and implement efficient algorithms. This is a key aspect of computer science and will impress the examiner.
- Use Data Structures Effectively: Choose appropriate data structures to solve your problem efficiently. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different data structures is crucial.
- Implement Error Handling: Implement robust error handling to prevent your program from crashing or producing incorrect results.
- Optimize Your Code: Optimize your code for performance. This can involve using more efficient algorithms, reducing memory usage, or using compiler optimizations.
- Showcase Your Creativity: Don't be afraid to be creative and innovative in your project. Think outside the box and develop a unique solution to your problem.
- Client/Advisor Feedback: Actively seek and incorporate feedback from your client or advisor. This demonstrates that you're taking their needs into account and improving your project based on their input. This is directly related to Criterion E: Evaluation, where feedback from the client/advisor is essential.
Example: If you're developing a game, consider implementing AI for the opponents or using procedural generation to create unique levels.
Technology and Modern Assessment Section
Technology is rapidly transforming the way we learn and assess computer science. AI-powered tools are becoming increasingly prevalent in education, offering new ways to provide personalized feedback and support student learning.
Marksy, as a leading AI grading assistant, is designed to help IB teachers provide consistent, detailed feedback on IA assessments. Marksy uses official IB criteria to ensure accuracy and fairness, saving educators valuable time while maintaining assessment quality. The platform provides rubric-aligned scoring, detailed criterion-by-criterion feedback, and suggestions for improvement, helping students understand exactly how to improve their work. This is especially useful in evaluating complex projects based on Criterion D: Functionality and Extensibility of Product, where assessing the potential for future development can be subjective. Marksy helps standardize this assessment.
By leveraging AI, teachers can focus on providing personalized guidance and support to their students, fostering a deeper understanding of computer science concepts. Students, in turn, receive more targeted feedback, enabling them to identify their strengths and weaknesses and improve their performance.
Conclusion with Clear Next Steps
Choosing the right programming language for your IB Computer Science IA is a critical decision that can significantly impact your grade. By carefully considering your skills, the complexity of your project, and the language's suitability for the chosen application, you can set yourself up for success. Remember to plan your project thoroughly, test your code rigorously, and document your work clearly.
Next Steps:
- Brainstorm Project Ideas: Explore different project ideas that align with your interests and skills.
- Research Programming Languages: Research the strengths and weaknesses of different programming languages and choose the one that best suits your project.
- Create a Detailed Plan: Develop a detailed plan outlining your goals, tasks, and timeline.
- Start Coding: Start coding your project and regularly seek feedback from your teacher or advisor.
- Evaluate Your Progress: Regularly evaluate your progress and make adjustments as needed.
Ready to take your IB Computer Science IA to the next level? Try Marksy for free today and experience the power of AI-driven feedback to improve your scores and streamline your grading workflow!