How to Use Economic Theory and Models in Your EE
Are you an IB student struggling to effectively incorporate economic theory and models into your Extended Essay (EE)? You're not alone! This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to select relevant theories, apply them rigorously, and analyze your findings to achieve a high score. We'll break down complex concepts into manageable steps, provide practical examples, and highlight common pitfalls to avoid, ensuring your EE demonstrates a strong understanding and critical application of economic principles. Let's dive in and unlock the secrets to a successful Economics EE!
Introduction (Answer the Query Immediately)
The IB Economics Extended Essay (EE) requires you to conduct independent research and present a well-structured, analytical argument. A crucial element of a successful EE is the appropriate and effective use of economic theory and models. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to select, apply, and analyze economic theories and models within the context of your EE. We will cover everything from choosing a suitable topic to critically evaluating your findings, ensuring you understand how to meet the IB's assessment criteria and maximize your score. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of how to integrate economic principles into your EE to create a compelling and insightful piece of academic work.
Struggling with IB Assessments?
Get instant, detailed feedback on your work with AI that understands IB criteria.
Core Content Sections
Choosing a Suitable Topic and Research Question
The foundation of a strong Economics EE lies in selecting a focused and manageable topic. Your research question should be specific, allowing you to delve deep into the issue and apply relevant economic theories.
- Specificity is Key: Avoid overly broad topics like "The Impact of Globalization." Instead, consider a more specific question like "To what extent has the implementation of tariffs on imported steel impacted the domestic steel industry in the United States between 2018 and 2023?"
- Economic Relevance: Ensure your topic is firmly rooted in economic principles. It should allow you to explore concepts like supply and demand, market structures, government intervention, or macroeconomic indicators.
- Data Availability: Choose a topic where you can access reliable data. This could include government statistics, academic research, or industry reports.
- Personal Interest: Select a topic that genuinely interests you. This will make the research process more engaging and help you stay motivated.
Example:
- Weak Research Question: "What are the effects of inflation?" (Too broad)
- Strong Research Question: "To what extent has quantitative easing by the European Central Bank (ECB) impacted inflation rates in Germany between 2015 and 2020?" (Specific, economically relevant, and allows for data analysis)
Selecting Relevant Economic Theories and Models
Once you have a research question, identify the economic theories and models that are most relevant to addressing it.
- Identify Core Concepts: Determine the key economic concepts at play in your research question. For example, if you're investigating the impact of minimum wage laws, you'll need to understand labor market theory, supply and demand, and potential efficiency losses.
- Choose Appropriate Models: Select models that can help you analyze the relationship between variables. This could include:
- Supply and Demand Model: Useful for analyzing price and quantity changes in markets.
- Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand (AS-AD) Model: Useful for analyzing macroeconomic issues like inflation and unemployment.
- Production Possibility Frontier (PPF): Useful for illustrating opportunity costs and economic efficiency.
- Game Theory: Useful for analyzing strategic interactions between economic agents.
- Justify Your Choices: Explain why you selected these specific theories and models. How do they help you answer your research question?
Example:
- Research Question: "To what extent has the introduction of a carbon tax impacted the consumption of gasoline in Canada between 2010 and 2020?"
- Relevant Theories and Models:
- Price Elasticity of Demand: To understand how responsive gasoline consumption is to price changes.
- Market Failure: To explain the negative externalities associated with gasoline consumption.
- Supply and Demand Model: To analyze the impact of the carbon tax on the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline.
Applying Economic Theories and Models
This is where you demonstrate your understanding of the chosen theories and models by applying them to your research question.
- Clearly Define Variables: Define all the variables you are using in your analysis. For example, if you're using a supply and demand model, clearly define the price and quantity of the good or service you are analyzing.
- Use Diagrams Effectively: Diagrams are powerful tools for illustrating economic concepts. Ensure your diagrams are accurately drawn, labeled, and explained.
- Support with Evidence: Back up your theoretical analysis with real-world data. This could include statistical data, case studies, or examples from academic research.
- Show Causation, Not Just Correlation: Don't simply state that two variables are related. Demonstrate how one variable influences the other, using economic theory to explain the causal mechanism.
Example:
Using a supply and demand diagram to illustrate the impact of a carbon tax:
- Draw the Initial Equilibrium: Draw the initial supply and demand curves for gasoline, showing the equilibrium price and quantity.
- Show the Impact of the Tax: Illustrate how the carbon tax shifts the supply curve to the left, increasing the price of gasoline and decreasing the quantity consumed.
- Explain the Diagram: Explain how the carbon tax internalizes the negative externality associated with gasoline consumption, leading to a more socially optimal outcome.
- Provide Data: Support your analysis with data on gasoline consumption and carbon tax rates in Canada between 2010 and 2020.
Analyzing and Evaluating Your Findings
The analysis and evaluation section is where you demonstrate your critical thinking skills.
- Interpret Your Results: What do your findings tell you about your research question? Do they support or contradict your initial hypothesis?
- Consider Limitations: Acknowledge the limitations of your research. What factors might have influenced your results? Are there any assumptions you made that could have affected your conclusions?
- Evaluate the Effectiveness of Policies: If your research question involves a policy intervention, evaluate its effectiveness. Did it achieve its intended goals? What were the unintended consequences?
- Offer Alternative Perspectives: Consider alternative perspectives on the issue. Are there other economic theories or models that could provide a different explanation?
Example:
- Limitation: "This study only considers the impact of the carbon tax on gasoline consumption. It does not account for other factors that may have influenced gasoline consumption, such as changes in income levels or the availability of alternative transportation options."
- Alternative Perspective: "While the carbon tax is intended to reduce gasoline consumption, some economists argue that it is a regressive tax that disproportionately affects low-income households. Alternative policies, such as subsidies for electric vehicles, may be more effective at reducing emissions without placing a burden on the poor."
Common Challenges/Mistakes Section
Many IB students struggle with similar challenges when writing their Economics EE. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Descriptive vs. Analytical: A common pitfall is writing a descriptive essay rather than an analytical one. Focus on explaining why things happen, not just what happened. Use economic theory to analyze the relationships between variables and draw conclusions.
- Lack of Focus: Ensure your essay remains focused on your research question. Avoid tangents and irrelevant information.
- Poor Data Analysis: Use data effectively to support your arguments. Don't simply present data without analyzing it. Use statistical tools to identify trends and relationships.
- Ignoring Limitations: Failing to acknowledge the limitations of your research can weaken your argument. Be honest about the constraints of your study and how they might have affected your results.
- Incorrect Diagrams: Ensure your diagrams are accurately drawn and labeled. A poorly drawn diagram can undermine your credibility.
Pro Tip: Get AI-Powered Grading
Stop second-guessing your grades. Get instant feedback aligned with official IB rubrics.

Advanced Tips/Strategies Section
To take your Economics EE to the next level, consider these advanced tips:
- Use Econometrics: If you have a strong background in statistics, consider using econometric techniques to analyze your data. This can add rigor and sophistication to your analysis.
- Explore Behavioral Economics: Incorporate insights from behavioral economics to explain how psychological factors influence economic decision-making.
- Consider Dynamic Effects: Analyze how economic variables change over time. This can provide a more nuanced understanding of the issue you are investigating.
- Engage with Academic Literature: Read widely on your topic and cite relevant academic research. This will demonstrate your understanding of the existing literature and help you develop a more sophisticated argument.
- Develop a Counterargument: Anticipate potential criticisms of your argument and address them proactively. This will strengthen your analysis and demonstrate your critical thinking skills.
Technology and Modern Assessment Section
Technology is transforming the way we learn and assess economics. AI-powered tools are becoming increasingly valuable for both students and teachers. For example, AI can help students find relevant data, analyze statistical trends, and even generate economic diagrams.
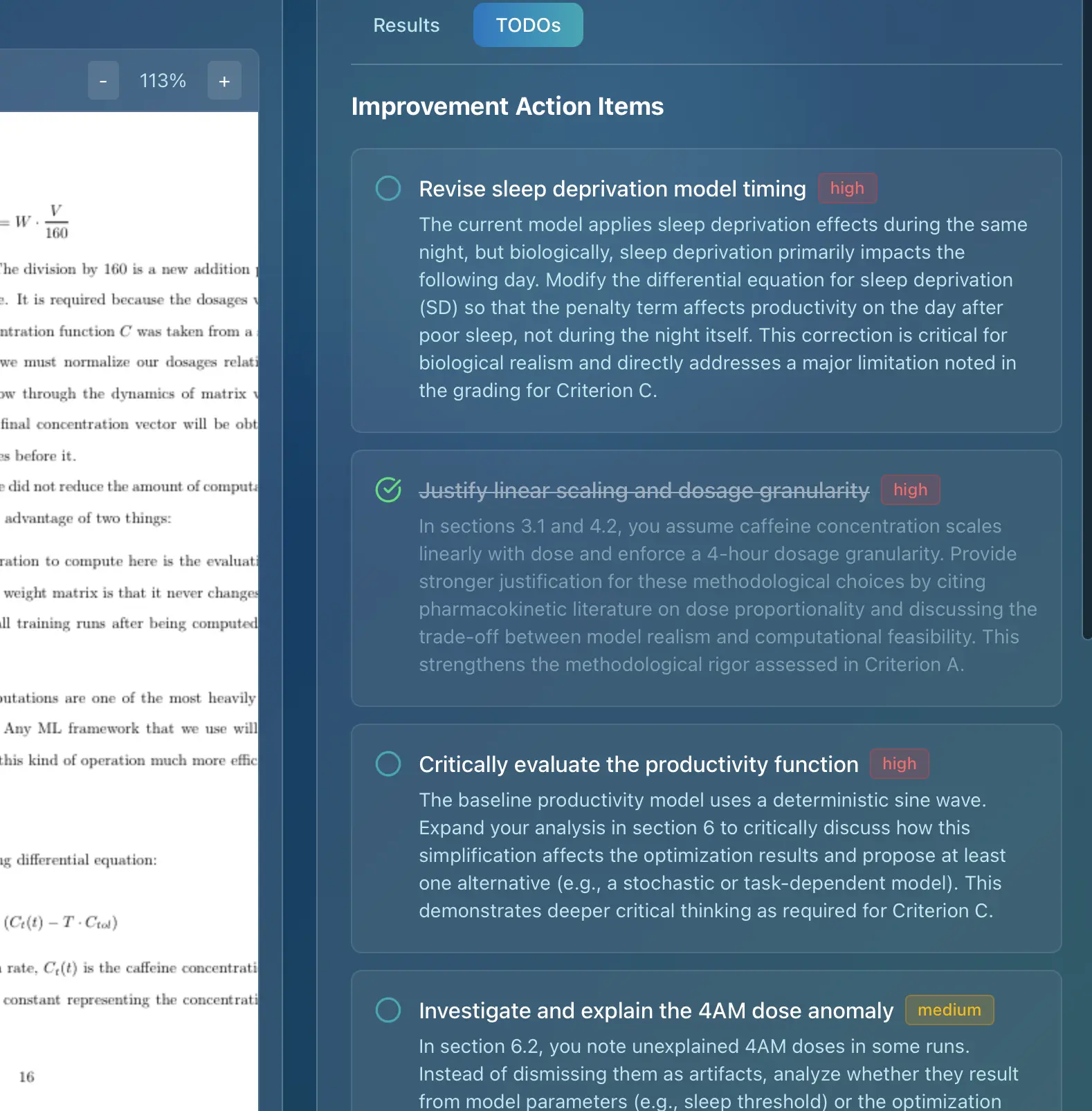
For teachers, AI grading assistants are revolutionizing the assessment process. Marksy, a leading AI grading assistant specifically designed for the International Baccalaureate, helps teachers provide consistent, detailed feedback on IB assessments like the Extended Essay. Marksy uses official IB rubrics to ensure accuracy and fairness, providing criterion-by-criterion feedback and suggestions for improvement. This not only saves teachers valuable time but also ensures that students receive high-quality, rubric-aligned feedback that helps them understand exactly how to improve their work. By automating the tedious aspects of grading, Marksy allows educators to focus on providing personalized support and guidance to their students. The use of AI in assessment is not about replacing teachers, but about empowering them to be more effective and efficient.
Conclusion with Clear Next Steps
Mastering the use of economic theory and models in your IB Economics Extended Essay is crucial for achieving a high score. By choosing a focused topic, selecting relevant theories, applying them rigorously, and analyzing your findings critically, you can demonstrate a strong understanding of economic principles and develop a compelling argument. Remember to avoid common mistakes, acknowledge limitations, and engage with academic literature to elevate your work.
Next Steps:
- Refine Your Research Question: Ensure your research question is specific, economically relevant, and allows for data analysis.
- Identify Relevant Theories: List the economic theories and models that are most relevant to your research question.
- Gather Data: Collect reliable data to support your analysis.
- Start Writing: Begin drafting your essay, focusing on the application of economic theories and models.
- Seek Feedback: Ask your teacher or a peer to review your essay and provide feedback.
- Try Marksy for Free: See how Marksy can help you improve your IB scores or streamline your grading workflow. Sign up for a free trial today and experience the power of AI-powered assessment!