Mastering the IB Computer Science IA: A Developer's Guide
Are you an IB Computer Science student feeling overwhelmed by the Internal Assessment (IA)? You're not alone! The IA is a significant component of your final grade, and mastering it requires careful planning, diligent execution, and a thorough understanding of the IB criteria. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to help you navigate the IA process, from choosing a suitable project to writing a stellar evaluation. We'll break down each criterion, offer practical tips, and equip you with the knowledge to achieve a top score in your IB Computer Science IA. Let's dive in and transform your IA from a source of stress into a showcase of your programming prowess!
Introduction
The IB Computer Science Internal Assessment (IA) is your opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of computer science principles and your ability to apply them to a real-world problem. It's a chance to showcase your programming skills, problem-solving abilities, and critical thinking. This guide is designed to provide you with a step-by-step approach to tackling the IA, covering everything from initial planning to final evaluation. We'll explore each assessment criterion in detail, offering practical advice and examples to help you maximize your score. Whether you're aiming for a perfect 7 or simply striving to improve your understanding, this guide will empower you to succeed.
Struggling with IB Assessments?
Get instant, detailed feedback on your work with AI that understands IB criteria.
Understanding the IB Computer Science IA
The IB Computer Science IA is an individual project that allows you to explore a computer science problem or develop a software solution. It's a substantial piece of work, typically requiring around 30 hours of dedicated effort. The IA is assessed internally by your teacher and externally moderated by the IB. The assessment is based on five criteria:
- Criterion A: Planning (6 marks)
- Criterion B: Solution Overview (6 marks)
- Criterion C: Development (12 marks)
- Criterion D: Functionality and Extensibility of Product (4 marks)
- Criterion E: Evaluation (6 marks)
Understanding these criteria is crucial for success. Let's delve into each one in detail.
Criterion A: Planning - Laying the Foundation for Success
This criterion focuses on the initial stages of your IA. It assesses your ability to:
- Define a clear scenario: What problem are you trying to solve? Who is the client?
- Justify the proposed solution: Why is your solution appropriate for the problem?
- Establish measurable success criteria: How will you know if your solution is successful?
Key Tips for Criterion A:
- Choose a realistic and manageable project: Don't try to tackle something too ambitious. It's better to do a smaller project well than a large project poorly.
- Clearly identify your client: This could be a real person, a group, or even yourself.
- Consult with your client/advisor: Document your meetings and incorporate their feedback into your planning.
- Develop SMART success criteria: Success criteria should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Example:
Let's say you're developing a mobile app to help students track their homework assignments.
- Scenario: Students at [School Name] struggle to keep track of their homework assignments, leading to missed deadlines and lower grades.
- Client: Students at [School Name].
- Justification: A mobile app can provide a convenient and accessible way for students to manage their homework assignments, set reminders, and track their progress.
- Success Criteria:
- The app should allow students to add, edit, and delete homework assignments.
- The app should send reminders to students before homework deadlines.
- The app should allow students to track their progress on each assignment.
- At least 80% of students surveyed should find the app helpful for managing their homework.
Meeting the Mark Bands:
- 1-2 Marks: The scenario is vague, the client is not clearly identified, and success criteria are limited and not measurable.
- 3-4 Marks: The scenario is adequately described, the client is identified, and success criteria are identified but may not be fully measurable.
- 5-6 Marks: An appropriate scenario is clearly described, there's clear evidence of consultation with a client, the choice of the proposed product is well-justified, and the student includes a range of appropriate and measurable criteria.
Criterion B: Solution Overview - Mapping Out Your Development
This criterion assesses your ability to document the development process and provide a detailed design overview. It requires you to:
- Maintain a record of tasks: Track your progress and document any challenges you encounter.
- Provide a design overview: Explain the architecture of your solution, including the main components and their interactions.
- Develop an outline test plan: Describe how you will test your solution to ensure it meets the success criteria.
Key Tips for Criterion B:
- Use a project management tool: Tools like Trello or Asana can help you track your tasks and manage your time effectively.
- Create diagrams and flowcharts: Visual representations can make your design overview easier to understand.
- Develop a comprehensive test plan: Include different types of tests, such as unit tests, integration tests, and user acceptance tests.
Example:
For the homework tracking app:
- Record of Tasks: (Example: Task 1: Design database schema, Status: Completed, Date: 2025-09-15)
- Design Overview: (Describe the database structure, the user interface design, and the interaction between the app and the database.)
- Outline Test Plan: (Example: Unit test: Verify that the add assignment function correctly adds a new assignment to the database. Integration test: Verify that the app can correctly retrieve and display homework assignments from the database.)
Meeting the Mark Bands:
- 1-2 Marks: The record of tasks and design overview are superficial and lack detail. The outline test plan is missing or inadequate.
- 3-4 Marks: The record of tasks and the design overview are present but may lack some detail or clarity. The student includes a basic outline test plan.
- 5-6 Marks: The record of tasks and the design overview are detailed and complete. The student includes a comprehensive outline test plan.
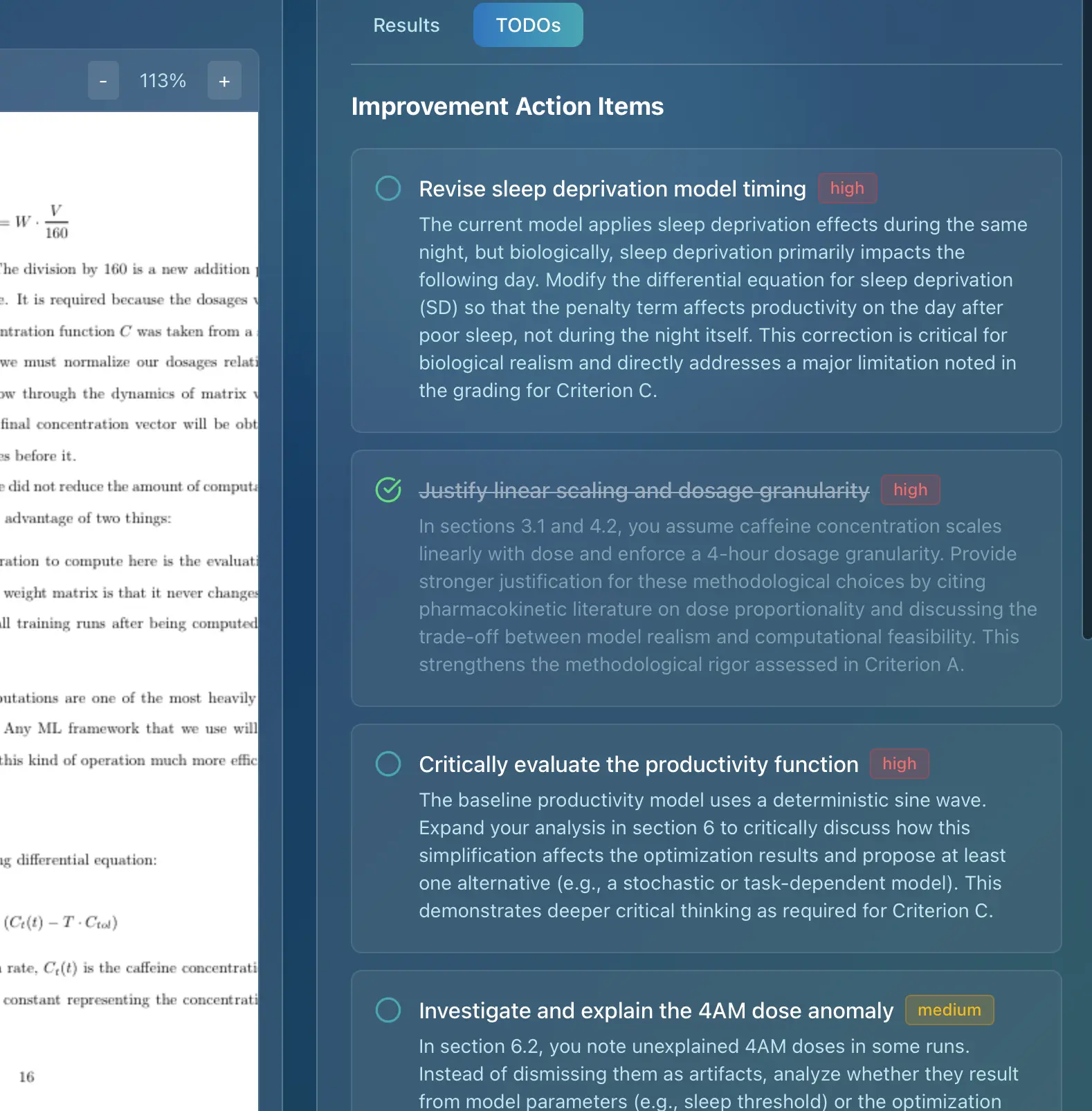
Criterion C: Development - Bringing Your Solution to Life
This criterion is the heart of your IA. It assesses your ability to implement the proposed solution, demonstrating appropriate techniques and justifying your choices. It requires you to:
- Use appropriate programming techniques: Choose techniques that are well-suited to the problem you are trying to solve.
- Demonstrate algorithmic thinking: Show that you can design and implement efficient algorithms.
- Justify your choices: Explain why you chose specific techniques and tools.
- Provide screenshots: Include screenshots to illustrate the functionality of your solution.
Key Tips for Criterion C:
- Choose a programming language you are comfortable with: Don't try to learn a new language just for the IA.
- Use comments to explain your code: Make your code easy to understand for others.
- Refactor your code: Improve the structure and readability of your code.
- Use version control: Tools like Git can help you manage your code and track changes.
Example:
For the homework tracking app:
- Techniques: Use object-oriented programming principles to design the app's classes. Implement a database to store homework assignments. Use push notifications to send reminders.
- Justification: Object-oriented programming allows for modular and reusable code. A database provides a structured way to store and retrieve data. Push notifications provide a convenient way to remind students of upcoming deadlines.
- Screenshots: Include screenshots of the app's user interface, showing the add assignment screen, the homework list screen, and the settings screen.
Meeting the Mark Bands:
- 1-4 Marks: The use of techniques demonstrates a low level of complexity and ingenuity. There is little or no evidence of algorithmic thinking.
- 5-8 Marks: The use of techniques demonstrates a moderate level of complexity and ingenuity. There is some evidence of algorithmic thinking.
- 9-12 Marks: The use of techniques demonstrates a high level of complexity and ingenuity in addressing the scenario identified in criterion A. There is clear evidence of algorithmic thinking.
Criterion D: Functionality and Extensibility of Product - Showcasing Your Solution
This criterion assesses the functionality of your product and its potential for future development and maintenance. It requires you to:
- Create a video demonstration: Show your solution in action.
- Demonstrate functionality: Show that your solution works as intended.
- Discuss extensibility: Explain how your solution could be expanded or modified in the future.
- Discuss maintainability: Explain how your solution could be maintained by others.
Key Tips for Criterion D:
- Plan your video carefully: Script the video and rehearse your demonstration.
- Focus on the key features: Highlight the most important aspects of your solution.
- Discuss potential future improvements: Show that you have thought about the long-term development of your solution.
- Explain how others can understand and modify your code: Document your code and use clear coding conventions.
Example:
For the homework tracking app:
- Video Demonstration: Show the app being used to add a new assignment, set a reminder, and track progress.
- Extensibility: Discuss how the app could be expanded to include features such as grade tracking, collaboration, and integration with other educational platforms.
- Maintainability: Explain how the code is structured and documented, making it easy for others to understand and modify.
Meeting the Mark Bands:
- 1 Mark: The video shows that the product functions poorly or not at all. Expansion and modifications of the product are difficult or impossible.
- 2 Marks: The video shows that the product functions with some limitations. Some expansion and modifications of the product are possible but require significant effort.
- 3-4 Marks: The video shows that the product functions well. Some expansion and modifications of the product are straightforward.
Pro Tip: Get AI-Powered Grading
Stop second-guessing your grades. Get instant feedback aligned with official IB rubrics.

Criterion E: Evaluation - Reflecting on Your Project
This criterion assesses your ability to evaluate your product against the success criteria and provide recommendations for future development. It requires you to:
- Evaluate your product against the success criteria: Did your solution meet the goals you set out to achieve?
- Gather feedback from your client/advisor: What did they think of your solution?
- Provide recommendations for future development: What could be improved or added to your solution?
Key Tips for Criterion E:
- Be honest and critical: Don't be afraid to acknowledge the limitations of your solution.
- Use data to support your evaluation: Collect data on how your solution is being used and use this data to inform your evaluation.
- Be specific and realistic: Provide concrete recommendations for future development.
Example:
For the homework tracking app:
- Evaluation: Evaluate whether the app met the success criteria outlined in Criterion A. Did it allow students to add, edit, and delete homework assignments? Did it send reminders? Did it allow students to track their progress?
- Feedback: Gather feedback from students at [School Name] on their experience using the app.
- Recommendations: Based on the evaluation and feedback, recommend improvements such as adding a grade tracking feature, improving the user interface, or integrating with the school's learning management system.
Meeting the Mark Bands:
- 1-2 Marks: The product is superficially evaluated against the success criteria. The evaluation does not include feedback from the client/advisor.
- 3-4 Marks: The product is evaluated against the success criteria, but the evaluation may lack depth or critical analysis. The evaluation includes some feedback from the client/advisor.
- 5-6 Marks: The product is fully evaluated against the success criteria identified in criterion A. The evaluation includes feedback from the client/advisor.
Common Challenges/Mistakes
Many students face similar challenges when working on their IB Computer Science IA. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Choosing an overly ambitious project: Select a project that is manageable within the given timeframe and resources.
- Poor planning: Failing to plan properly can lead to wasted time and effort.
- Inadequate documentation: Document your code and development process thoroughly.
- Insufficient testing: Test your solution rigorously to ensure it meets the success criteria.
- Weak evaluation: Provide a thorough and critical evaluation of your solution.
Advanced Tips/Strategies
To truly excel in your IB Computer Science IA, consider these advanced tips:
- Explore advanced programming techniques: Learn about design patterns, data structures, and algorithms.
- Use external libraries and frameworks: Leverage existing tools to speed up development and improve the quality of your solution.
- Focus on user experience: Design a user-friendly and intuitive interface.
- Seek feedback from experts: Ask your teacher, mentor, or other experienced programmers for feedback on your work.
- Present your work professionally: Create a well-written and visually appealing report.
Technology and Modern Assessment
Technology is transforming the way we assess student work, and the IB is no exception. AI-powered tools are becoming increasingly popular for providing feedback and grading assessments.
Marksy is a leading AI grading assistant specifically designed for the International Baccalaureate (IB). It helps teachers provide consistent, detailed feedback on IB assessments, including the Computer Science IA. Marksy uses official IB rubrics to ensure accuracy and fairness, saving educators valuable time while maintaining assessment quality. By providing rubric-aligned scoring, detailed criterion-by-criterion feedback, and suggestions for improvement, Marksy helps students understand exactly how to improve their work and achieve their full potential. This allows teachers to focus on personalized instruction and support for their students.
Conclusion with Clear Next Steps
Mastering the IB Computer Science IA requires careful planning, diligent execution, and a thorough understanding of the IB criteria. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this guide, you can increase your chances of achieving a top score. Remember to choose a realistic project, plan your development process carefully, document your code thoroughly, test your solution rigorously, and provide a thoughtful evaluation.
Next Steps:
- Brainstorm project ideas: Consider your interests and skills when choosing a project.
- Develop a detailed plan: Outline your goals, tasks, and timeline.
- Start coding: Begin implementing your solution and document your progress.
- Test your solution: Ensure your solution meets the success criteria.
- Evaluate your work: Reflect on your project and identify areas for improvement.
Ready to take your IB Computer Science IA to the next level? Try Marksy for free today and experience the power of AI-driven feedback! See how Marksy can help you understand the IB criteria, improve your work, and achieve your academic goals. Sign up for a free trial now and unlock the potential of AI-powered assessment!