The Ultimate IB Math IA Checklist: Don't Lose Easy Marks
Struggling to navigate the IB Math IA? You're not alone! The Internal Assessment is a significant component of your final IB Math grade, and often students lose marks on easily avoidable mistakes. This ultimate checklist is designed to guide you through every stage of the process, from choosing a topic to polishing your final submission. We'll break down the IB Math IA criteria, provide actionable tips, and help you understand how to maximize your score, ensuring you don't lose those crucial "easy marks." This guide is your key to mastering the IB Math Internal Assessment.
Introduction: Your Path to IA Success Starts Here
The IB Math IA (Internal Assessment) is your opportunity to showcase your mathematical understanding and skills through an independent exploration. It's a chance to delve deeper into a topic that interests you, apply your knowledge, and demonstrate your problem-solving abilities. However, many students find the IA daunting, unsure of where to start or how to meet the IB's rigorous assessment criteria. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist to help you navigate the IA process with confidence, whether you're in Math AA (Analysis and Approaches) or AI (Applications and Interpretation), at either Standard Level (SL) or Higher Level (HL). We'll cover everything from selecting a suitable topic to ensuring your mathematical communication is crystal clear, helping you secure the best possible grade.
Struggling with IB Assessments?
Get instant, detailed feedback on your work with AI that understands IB criteria.
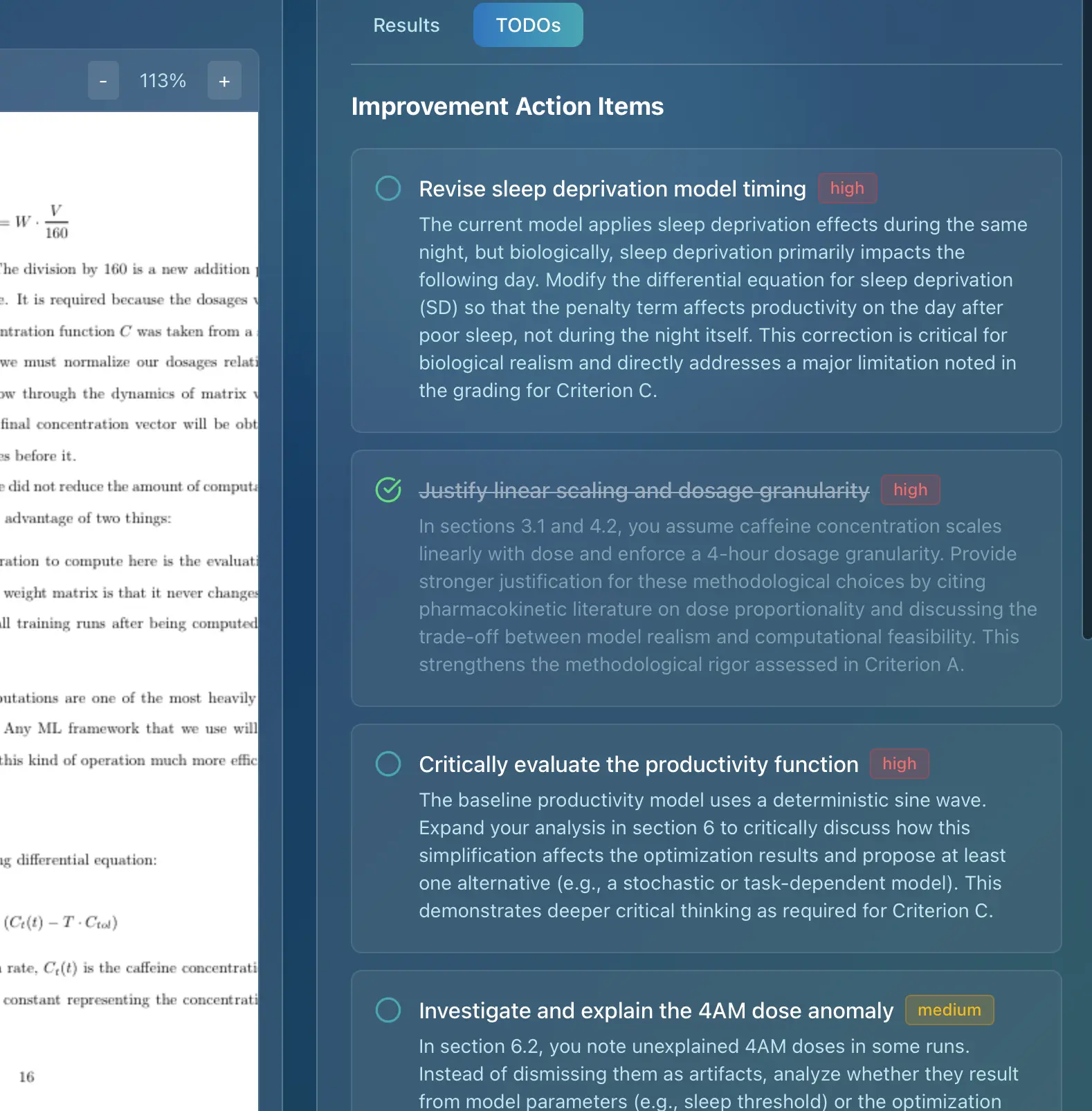
Core Content Sections: Mastering the IB Math IA Criteria
To achieve a high score on your IB Math IA, you need to understand and address each assessment criterion effectively. Let's break down each criterion and provide a checklist to guide you.
Criterion A: Presentation (0-4 marks) - Organization and Clarity
This criterion assesses how well your IA is organized, coherent, and concise. Think of it as the first impression your IA makes on the examiner.
Checklist for Criterion A:
- [ ] Clear Introduction: Does your introduction clearly state the topic, objectives, and research question?
- [ ] Logical Structure: Is your IA logically structured with a clear flow of ideas? Use headings and subheadings to guide the reader.
- [ ] Coherent Argument: Does your argument flow logically from one section to the next? Ensure each section builds upon the previous one.
- [ ] Concise Writing: Is your writing concise and to the point? Avoid unnecessary jargon or repetition.
- [ ] Visual Appeal: Is your IA visually appealing and easy to read? Use appropriate formatting, spacing, and visuals (graphs, diagrams) to enhance readability.
- [ ] Page Limit: Is your IA within the 12-20 page limit?
Example:
- Poor: A disorganized IA with rambling explanations and no clear structure.
- Good: An IA with a clear introduction, logically organized sections, and concise explanations, making it easy for the reader to follow the argument.
Criterion B: Mathematical Communication (0-4 marks) - Language and Notation
This criterion assesses your ability to use mathematical language, notation, and representations accurately and effectively.
Checklist for Criterion B:
- [ ] Accurate Notation: Are you using correct mathematical notation throughout your IA? Double-check your symbols, equations, and formulas.
- [ ] Defined Variables: Are all variables clearly defined? Use a "Nomenclature" section if necessary.
- [ ] Clear Explanations: Are your mathematical calculations and processes clearly explained? Don't assume the reader knows what you're doing.
- [ ] Appropriate Language: Are you using appropriate mathematical language and terminology? Avoid colloquialisms or informal language.
- [ ] Multiple Representations: Are you using multiple forms of mathematical representation (e.g., graphs, tables, equations) to support your argument?
- [ ] Proper Labeling: Are all graphs, tables, and diagrams properly labeled with clear titles and axes?
- [ ] Deductive Reasoning: If applicable, does your IA demonstrate the use of deductive reasoning and logical proofs?
Example:
- Poor: Using incorrect notation, failing to define variables, and providing unclear explanations of mathematical processes.
- Good: Using accurate notation, clearly defining all variables, providing detailed explanations of mathematical processes, and using multiple forms of representation to support the argument.
Criterion C: Personal Engagement (0-3 marks) - Your Connection to the Topic
This criterion assesses the extent to which you demonstrate personal engagement with the exploration. It's about showing your passion and interest in the topic.
Checklist for Criterion C:
- [ ] Topic Selection: Did you choose a topic that genuinely interests you? This will make the exploration more enjoyable and engaging.
- [ ] Personal Connection: Can you explain why you chose this topic and how it relates to your personal interests or experiences?
- [ ] Predictions and Testing: Did you formulate predictions and test their validity? This shows a deeper level of engagement.
- [ ] Diverse Perspectives: Did you consider different perspectives or approaches to the problem?
- [ ] Independent Thinking: Does your IA demonstrate independent thinking and creativity?
- [ ] Originality: Does your IA demonstrate originality in the approach or analysis?
Example:
- Poor: Choosing a generic topic and simply following a textbook example without any personal connection or original thought.
- Good: Choosing a topic related to a personal interest (e.g., analyzing the mathematics of a sport you play) and demonstrating independent thinking by formulating predictions and testing their validity.
Criterion D: Reflection (0-3 marks) - Critical Analysis and Evaluation
This criterion assesses the extent to which you reflect on the process, results, and implications of your exploration. It's about showing your critical thinking skills.
Checklist for Criterion D:
- [ ] Strengths and Weaknesses: Did you identify the strengths and weaknesses of your mathematical approaches?
- [ ] Limitations: Did you acknowledge the limitations of your investigation?
- [ ] Impact of Results: Did you evaluate the impact of your results?
- [ ] Rational Extensions: Did you propose rational extensions to the study?
- [ ] Conclusion: Does your conclusion link back to your research question and the aims of the investigation?
- [ ] Alternative Approaches: Did you consider alternative approaches or methods that could have been used?
- [ ] Real-World Implications: Did you discuss the real-world implications of your findings?
Example:
- Poor: Simply stating the results without any critical analysis or evaluation of the process or limitations.
- Good: Discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the chosen mathematical methods, acknowledging the limitations of the investigation, and proposing rational extensions to the study.
Criterion E: Use of Mathematics (SL/HL) (0-6 marks) - Application and Understanding
This criterion assesses the appropriateness, correctness, and level of mathematical understanding demonstrated in your exploration. The expectations differ between Standard Level (SL) and Higher Level (HL).
Checklist for Criterion E (SL):
- [ ] Relevant Mathematics: Is the mathematics used relevant to the topic and commensurate with the SL syllabus?
- [ ] Correctness: Is the mathematics used correct and accurate?
- [ ] Understanding: Does your IA demonstrate a thorough understanding of the mathematical concepts involved?
- [ ] Explanations: Are all calculations and processes clearly explained?
- [ ] Avoid Complexity: Is unnecessarily complex mathematics avoided?
- [ ] Approximation: Are approximations used appropriately and justified?
Checklist for Criterion E (HL):
- [ ] HL Level Mathematics: Is the mathematics used part of the HL syllabus or at a similar level?
- [ ] Correctness: Is the mathematics used error-free and accurate?
- [ ] Understanding: Does your IA demonstrate a sophisticated understanding of the mathematical concepts involved?
- [ ] Explanations: Are all calculations and processes clearly explained?
- [ ] Sophistication: Does your IA demonstrate sophistication by using challenging mathematical concepts, looking at the problem from different perspectives, or linking different areas of mathematics together?
- [ ] Justification/Proofs: Are mathematical claims relevant to the investigation justified or proven?
- [ ] Approximation: Are approximations used appropriately and justified?
Example:
- Poor: Using incorrect mathematics, failing to demonstrate understanding of the concepts, or using mathematics that is not relevant to the topic.
- Good: Using relevant and correct mathematics, demonstrating a thorough understanding of the concepts, providing clear explanations of all calculations, and, for HL, demonstrating sophistication by using challenging concepts and justifying mathematical claims.
Common Challenges/Mistakes Section: Avoiding Pitfalls
Many students make common mistakes that can cost them valuable marks. Here's a list of common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Choosing a Topic That Is Too Broad: Narrow down your topic to something manageable within the word limit.
- Lack of Personal Engagement: Choose a topic that genuinely interests you to make the exploration more engaging and original.
- Poor Mathematical Communication: Use accurate notation, define variables, and provide clear explanations of all calculations.
- Insufficient Reflection: Critically analyze the strengths and weaknesses of your approaches, acknowledge limitations, and propose rational extensions.
- Using Inappropriate Mathematics: Ensure the mathematics used is relevant to the topic and commensurate with your level (SL or HL).
- Ignoring the Rubric: Familiarize yourself with the IB Math IA rubric and use it as a guide throughout the process.
- Plagiarism: Ensure all sources are properly cited to avoid plagiarism.
- Procrastination: Start early and manage your time effectively to avoid rushing the IA at the last minute.
Pro Tip: Get AI-Powered Grading
Stop second-guessing your grades. Get instant feedback aligned with official IB rubrics.

Advanced Tips/Strategies Section: Elevate Your IA
Ready to take your IA to the next level? Here are some advanced tips and strategies:
- Explore Beyond the Syllabus (HL): For HL students, consider exploring mathematical concepts beyond the syllabus to demonstrate sophistication.
- Use Technology Effectively: Utilize graphing calculators, software packages (e.g., GeoGebra, Mathematica), or programming languages (e.g., Python) to enhance your analysis.
- Seek Feedback Early and Often: Ask your teacher or peers to review your IA at various stages of the process and provide constructive feedback.
- Focus on Depth Over Breadth: Instead of trying to cover too much ground, focus on exploring a specific aspect of your topic in depth.
- Connect to Real-World Applications: Whenever possible, connect your mathematical findings to real-world applications to demonstrate relevance.
- Consider Interdisciplinary Connections: Explore connections between your IA topic and other subjects you are studying.
Technology and Modern Assessment Section: AI and the Future of IB Grading
Technology is transforming the way IB assessments are graded, offering new tools and resources for both students and teachers. AI-powered grading assistants are becoming increasingly popular, providing instant, accurate, and detailed feedback on student work.
Marksy is a leading AI grading assistant specifically designed for the International Baccalaureate (IB). It uses official IB rubrics to provide consistent, detailed feedback on IB assessments, including the Math IA. Marksy helps teachers save time by automating the grading process while ensuring accuracy and fairness. Students benefit from detailed criterion-by-criterion feedback and suggestions for improvement, allowing them to understand exactly how to improve their work. With Marksy, educators can focus on providing personalized support and guidance to their students, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter. AI tools like Marksy use official IB criteria to ensure accuracy and fairness, providing a valuable resource for both students and teachers.
Conclusion with Clear Next Steps: Your Journey to a Top Grade
The IB Math IA is a challenging but rewarding experience. By following this comprehensive checklist and avoiding common mistakes, you can significantly increase your chances of achieving a top grade. Remember to choose a topic that interests you, demonstrate personal engagement, communicate your mathematical ideas clearly, reflect critically on your process, and use appropriate mathematics.
Next Steps:
- Review the IB Math IA Rubric: Familiarize yourself with the assessment criteria.
- Brainstorm Potential Topics: Choose a topic that genuinely interests you and is manageable within the word limit.
- Create an Outline: Plan the structure of your IA and allocate time for each section.
- Start Writing: Begin working on your IA early and seek feedback from your teacher or peers.
- Revise and Edit: Carefully review your IA for errors in mathematics, grammar, and formatting.
- Submit Your IA: Submit your IA by the deadline.
Ready to experience the future of IB grading? Try Marksy for free today and see how it can help you improve your IB Math IA score or streamline your grading workflow! [Link to Marksy Free Trial]