Top 15 IB Math IA Topic Ideas (HL & SL)
Are you an IB Math student searching for the perfect Internal Assessment (IA) topic? Finding a suitable topic that allows you to demonstrate your mathematical skills and personal engagement can be challenging. This comprehensive guide provides 15 engaging and challenging IB Math IA topic ideas for both Higher Level (HL) and Standard Level (SL) students. We'll also delve into common mistakes, advanced strategies, and how AI can help you excel. Get ready to unlock your IA potential and achieve a top score!
Introduction (Answer the Query Immediately)
The IB Math Internal Assessment (IA) is a significant component of your final grade, requiring you to explore a mathematical topic of your choice. Choosing the right topic is crucial for success. This guide provides 15 diverse and engaging IB Math IA topic ideas suitable for both HL and SL students. We'll cover a range of mathematical areas, offering inspiration and guidance to help you select a topic that aligns with your interests and skills. We'll also provide tips on how to avoid common pitfalls and maximize your score. Remember, a well-chosen topic, combined with a strong understanding of the IB Math IA criteria, is the key to achieving a high grade.
Struggling with IB Assessments?
Get instant, detailed feedback on your work with AI that understands IB criteria.

Core Content Sections
Understanding the IB Math IA Criteria
Before diving into topic ideas, it's essential to understand the IB Math IA assessment criteria. The IA is assessed based on five criteria:
- Criterion A: Presentation (0-4 marks): Focuses on the organization, coherence, and conciseness of your investigation. A well-structured IA is easy to follow and understand.
- Criterion B: Mathematical Communication (0-4 marks): Assesses the appropriate use of mathematical language, notation, and representations. Clarity and accuracy are paramount.
- Criterion C: Personal Engagement (0-3 marks): Evaluates the extent to which you demonstrate personal interest and involvement in the exploration.
- Criterion D: Reflection (0-3 marks): Examines your ability to reflect on the process, results, and implications of your investigation.
- Criterion E: Use of Mathematics (SL: 0-6 marks, HL: 0-6 marks): Assesses the appropriateness, correctness, and level of mathematical understanding demonstrated. HL IAs are expected to demonstrate a higher level of mathematical sophistication and rigor.
Choosing the Right Topic: Key Considerations
When selecting your IB Math IA topic, consider the following:
- Your Interests: Choose a topic that genuinely interests you. This will make the research process more enjoyable and lead to a more engaging IA.
- Mathematical Suitability: Ensure the topic allows you to apply relevant mathematical concepts and techniques from the IB Math syllabus.
- Data Availability: Consider whether you can access sufficient data to support your investigation.
- Scope and Complexity: Choose a topic that is neither too broad nor too narrow. Aim for a manageable scope that allows for in-depth analysis.
- Personal Engagement: Select a topic that allows you to demonstrate personal engagement, such as formulating predictions or linking to personal interests.
Top 15 IB Math IA Topic Ideas (HL & SL)
Here are 15 IB Math IA topic ideas, categorized by mathematical area, suitable for both HL and SL students. Remember to adapt the complexity and scope of the topic to match your level.
1. Modeling the Spread of a Disease (Calculus/Statistics):
- Description: Investigate the spread of a disease using mathematical models like the SIR (Susceptible-Infected-Recovered) model. Analyze real-world data and explore the impact of different parameters on the spread of the disease.
- Mathematical Concepts: Differential equations, exponential functions, statistical analysis, modeling.
- HL Extension: Incorporate more complex models, such as SEIR (Susceptible-Exposed-Infected-Recovered) or agent-based models.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a simpler model and analyze data from a specific outbreak.
2. Optimizing a Real-World Process (Calculus/Optimization):
- Description: Identify a real-world process, such as optimizing the delivery route for a company or maximizing the profit of a business, and develop a mathematical model to optimize it.
- Mathematical Concepts: Optimization techniques, linear programming, calculus, constraints.
- HL Extension: Use Lagrange multipliers or more advanced optimization algorithms.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a simpler process with fewer variables.
3. Analyzing Financial Markets (Statistics/Probability):
- Description: Investigate patterns and trends in financial markets using statistical analysis and probability. Analyze stock prices, currency exchange rates, or other financial data.
- Mathematical Concepts: Statistical analysis, probability distributions, regression analysis, time series analysis.
- HL Extension: Explore more advanced statistical models, such as ARIMA models or GARCH models.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific stock or currency and analyze its historical performance.
4. Modeling Population Growth (Calculus/Differential Equations):
- Description: Investigate population growth using mathematical models like the logistic growth model. Analyze real-world population data and explore the impact of different factors on population growth.
- Mathematical Concepts: Differential equations, exponential functions, modeling.
- HL Extension: Incorporate factors like carrying capacity and environmental limitations.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific population and analyze its growth over a limited time period.
5. Investigating Fractals (Geometry/Calculus):
- Description: Explore the properties of fractals, such as the Mandelbrot set or the Sierpinski triangle. Investigate their self-similarity and fractal dimension.
- Mathematical Concepts: Geometry, complex numbers, limits, recursion.
- HL Extension: Explore the connection between fractals and chaos theory.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific fractal and analyze its properties.
6. The Mathematics of Cryptography (Number Theory/Modular Arithmetic):
- Description: Explore the mathematical principles behind cryptography, such as RSA encryption or Caesar ciphers.
- Mathematical Concepts: Number theory, modular arithmetic, prime numbers, algorithms.
- HL Extension: Investigate more advanced cryptographic algorithms, such as elliptic curve cryptography.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a simpler cipher and analyze its strengths and weaknesses.
7. Modeling Projectile Motion (Calculus/Physics):
- Description: Investigate the motion of a projectile, such as a ball thrown in the air. Develop a mathematical model to predict its trajectory and range.
- Mathematical Concepts: Calculus, kinematics, trigonometry, vectors.
- HL Extension: Incorporate factors like air resistance and wind.
- SL Adaptation: Simplify the model by neglecting air resistance.
8. Analyzing Game Theory (Probability/Logic):
- Description: Explore the mathematical principles behind game theory, such as the Prisoner's Dilemma or the Nash Equilibrium.
- Mathematical Concepts: Probability, logic, matrices, optimization.
- HL Extension: Investigate more complex games and strategies.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a simpler game and analyze its optimal strategies.
9. Exploring the Golden Ratio (Geometry/Number Theory):
- Description: Investigate the properties of the golden ratio and its appearance in nature, art, and architecture.
- Mathematical Concepts: Geometry, number theory, sequences, limits.
- HL Extension: Explore the connection between the golden ratio and Fibonacci numbers.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific example of the golden ratio in nature or art.
10. Modeling Traffic Flow (Calculus/Differential Equations):
- Description: Investigate traffic flow using mathematical models. Analyze real-world traffic data and explore the impact of different factors on traffic congestion.
- Mathematical Concepts: Differential equations, calculus, modeling.
- HL Extension: Incorporate more complex models, such as cellular automata models.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific road segment and analyze its traffic flow.
11. The Mathematics of Music (Trigonometry/Harmonic Analysis):
- Description: Explore the mathematical relationships between musical notes, scales, and harmonies.
- Mathematical Concepts: Trigonometry, harmonic analysis, Fourier series.
- HL Extension: Analyze the spectral content of different musical instruments.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific musical scale or chord and analyze its mathematical properties.
12. Investigating Voting Systems (Statistics/Probability):
- Description: Analyze different voting systems and their potential biases using statistical analysis and probability.
- Mathematical Concepts: Statistics, probability, combinatorics.
- HL Extension: Explore more advanced voting systems and their mathematical properties.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific voting system and analyze its potential biases.
13. Modeling Climate Change (Calculus/Statistics):
- Description: Investigate climate change using mathematical models. Analyze real-world climate data and explore the impact of different factors on global warming.
- Mathematical Concepts: Calculus, statistics, differential equations, modeling.
- HL Extension: Incorporate more complex climate models.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific aspect of climate change, such as sea level rise or temperature changes.
14. Analyzing Sports Statistics (Statistics/Probability):
- Description: Investigate patterns and trends in sports statistics using statistical analysis and probability. Analyze player performance, team strategies, or game outcomes.
- Mathematical Concepts: Statistical analysis, probability distributions, regression analysis.
- HL Extension: Develop predictive models for sports outcomes.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific sport and analyze its statistics.
15. The Mathematics of Art (Geometry/Transformations):
- Description: Explore the use of mathematical principles in art, such as perspective, symmetry, and tessellations.
- Mathematical Concepts: Geometry, transformations, trigonometry.
- HL Extension: Analyze the mathematical properties of specific artworks.
- SL Adaptation: Focus on a specific artistic technique and analyze its mathematical basis.
Common Challenges/Mistakes Section
Many students struggle with the IB Math IA due to common mistakes. Here are some to avoid:
- Poor Topic Choice: Selecting a topic that is too broad, too narrow, or doesn't allow for sufficient mathematical exploration.
- Solution: Carefully consider your interests and skills, and choose a topic that is manageable and allows for in-depth analysis.
- Lack of Personal Engagement: Failing to demonstrate personal interest and involvement in the exploration.
- Solution: Choose a topic that genuinely interests you and allows you to formulate predictions or link to personal interests.
- Inadequate Mathematical Communication: Using inappropriate mathematical language, notation, or representations.
- Solution: Ensure you use clear and accurate mathematical language, and properly label all diagrams and graphs. Review Criterion B in the IA Guide. For example, ensure you define all variables and explain your calculations.
- Insufficient Reflection: Failing to reflect on the process, results, and implications of the investigation.
- Solution: Discuss the strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of your approach, and link your conclusion to the research question.
- Incorrect or Inappropriate Mathematics: Using incorrect or inappropriate mathematical techniques.
- Solution: Ensure you have a strong understanding of the mathematical concepts and techniques you are using, and seek help from your teacher if needed.
- Poor Presentation: A disorganized, incoherent, or unclear IA.
- Solution: Plan your IA carefully, use clear headings and subheadings, and ensure your writing is concise and easy to understand.
Pro Tip: Get AI-Powered Grading
Stop second-guessing your grades. Get instant feedback aligned with official IB rubrics.
Advanced Tips/Strategies Section
To excel in your IB Math IA, consider these advanced tips:
- Start Early: Begin working on your IA well in advance of the deadline to allow ample time for research, analysis, and writing.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly seek feedback from your teacher and peers throughout the IA process.
- Use Technology Effectively: Utilize software like GeoGebra, Desmos, or Wolfram Alpha to aid in your analysis and visualization.
- Go Beyond the Syllabus: Demonstrate a deeper understanding of the mathematical concepts by exploring topics beyond the IB Math syllabus (HL only). Remember to clarify any mathematics that extends beyond the syllabus.
- Focus on Depth, Not Breadth: It's better to explore a topic in depth than to cover a wide range of topics superficially.
- Justify Your Choices: Clearly explain why you chose a particular approach or technique, and justify your assumptions.
- Connect to Real-World Applications: Whenever possible, connect your investigation to real-world applications to demonstrate the relevance of your work.
Technology and Modern Assessment Section
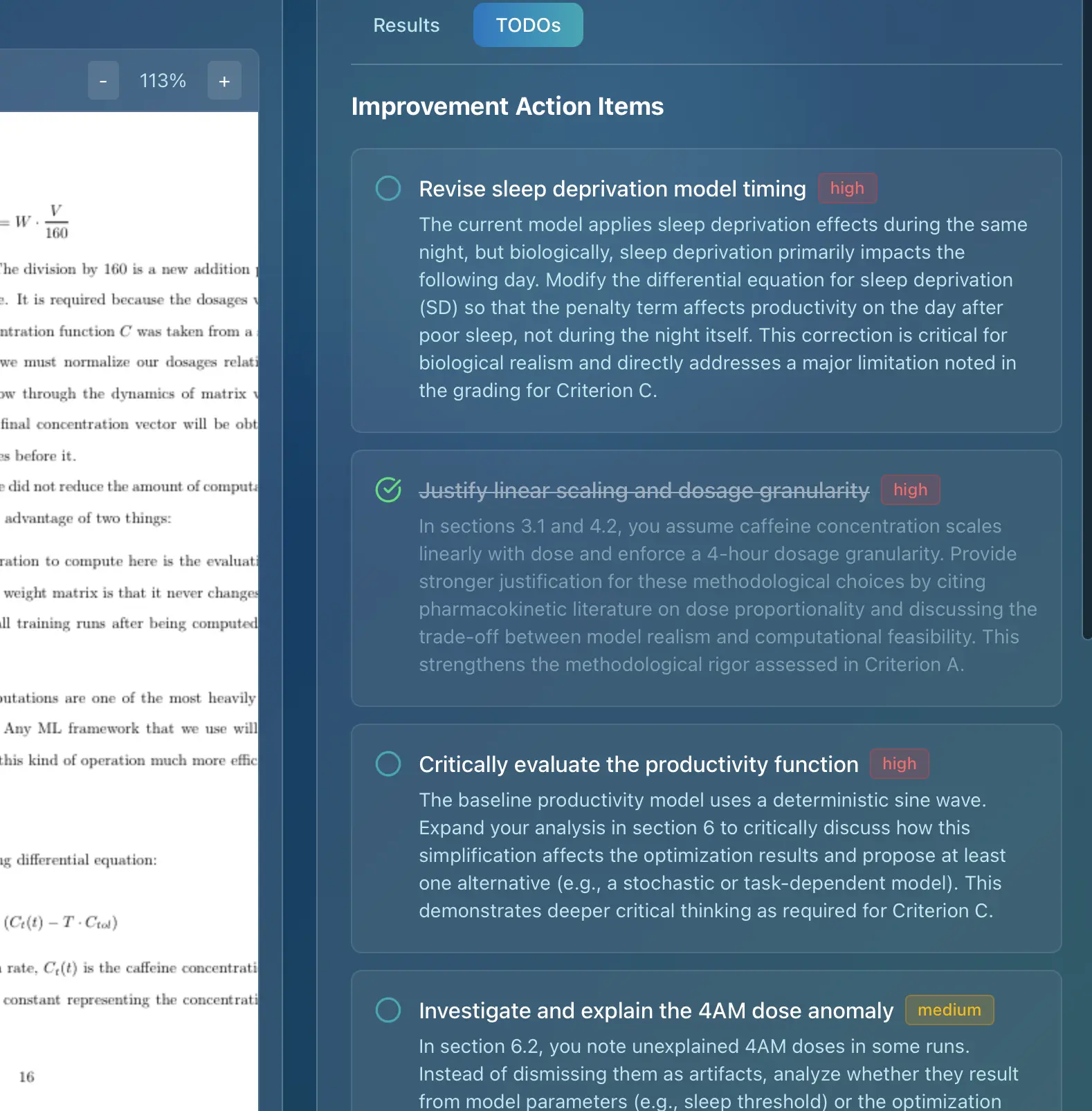
Technology is transforming IB assessment, and AI is playing an increasingly important role. Tools like Marksy, an AI grading assistant, are helping teachers provide consistent, detailed feedback on IB assessments. Marksy uses official IB criteria to ensure accuracy and fairness, saving educators valuable time while maintaining assessment quality.
For example, Marksy can analyze your IA draft and provide instant feedback on areas such as mathematical communication, presentation, and reflection, highlighting areas where you can improve to meet the specific requirements of the IB rubric. This allows you to refine your work and maximize your score.
Furthermore, AI tools can help teachers identify common errors and misconceptions among students, allowing them to tailor their instruction to address specific needs. This leads to more effective learning and improved student outcomes.
Conclusion with Clear Next Steps
Choosing the right IB Math IA topic is crucial for success. By considering your interests, skills, and the IB Math IA criteria, you can select a topic that allows you to demonstrate your mathematical abilities and achieve a top score. Remember to avoid common mistakes, seek feedback, and utilize technology effectively.
Ready to take your IB Math IA to the next level? Try Marksy for free today and experience the power of AI-driven feedback. Sign up for a free trial and see how Marksy can help you improve your IB scores or streamline your grading workflow. [Link to Marksy Free Trial]